The English language, belonging to the West Germanic group within the Indo-European language family, has a rich history that spans centuries and continents.
Name: English Language
Group: Germanic
Subgroup: West Germanic
Family: Indo-European
Region: United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Republic of Ireland, and various other countries
Script: Latin (English alphabet)
Official Language: United Nations, European Union, and many other international and regional organizations
Speakers: Over two billion (as of 2005)
Classification: Indo-European > Germanic > West Germanic
Closest Relatives: Frisian, Low German, Dutch, Scots
Development: Old English (c. 550–1066) > Middle English (c. 1066–1500) > Modern English (c. 1500–present)
Influences: Old Norse, Norman French, Latin, among others
Notable Works: Beowulf, King James Bible, works of William Shakespeare
Lingua Franca: Used in international discourse, science, navigation, law, and professional contexts
Grammar Evolution: From highly inflectional Old English to mostly analytic Modern English
Unique Features: Mix of vocabulary and grammar from various language influences
Mutual Intelligibility: Not mutually intelligible with continental Germanic languages
Dialect Continuum: Includes various dialects, including Scots
Key Features: Great Vowel Shift, Latin and Greek word borrowing, standardization of English spelling
Influential Periods: Viking invasions (8th to 12th centuries), Norman Conquest (1066), Great Vowel Shift (late 15th century)
Current Status: Most widely spoken language in the world, third most spoken native language
Other Info: Named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples in Britain. Speakers are called Anglophones. Co-official language in multiple countries. Affects 70% of Germanic language branch speakers.
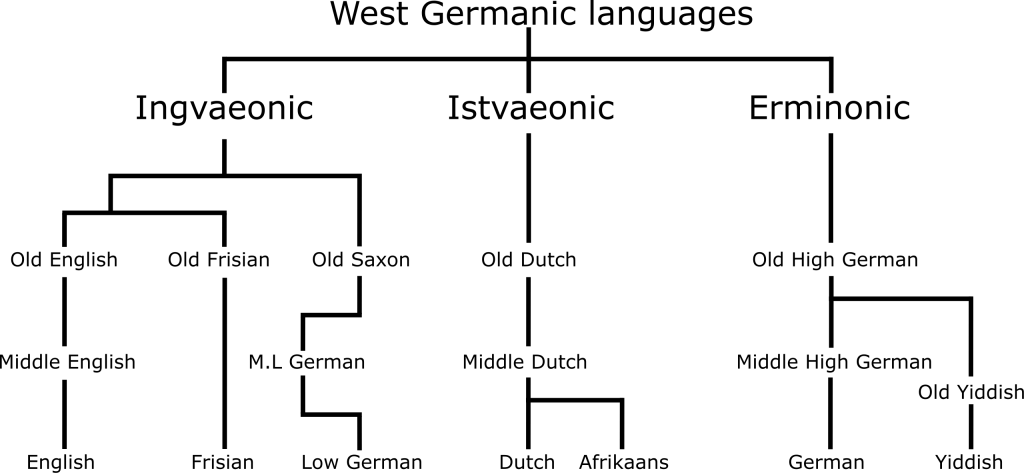
Ancient Origins
English has its roots in the early medieval period of England. It evolved from a group of dialects spoken by the West Germanic-speaking Anglo-Saxons who settled in Britain around the 5th century. These dialects gradually formed what is known as Old English, and the Old Norse language influenced them due to Viking settlements in the 8th and 9th centuries.
Medieval Influences
The Middle English period, which began in the late 11th century after the Norman Conquest of England, saw significant changes in the language. Old French, especially Old Norman French, and Latin-derived vocabulary were incorporated into English over several hundred years. This linguistic blend resulted in Middle English, characterized by a diverse language and complex word order.
The Renaissance and Modernization
The late 15th century marked the beginning of Early Modern English, a period that saw the Great Vowel Shift and an influx of Latin and Greek words, thanks to the Renaissance and the introduction of the printing press. This era is notable for producing works like the King James Bible and the writings of William Shakespeare. The printing press also played a pivotal role in standardizing English spelling, which remains unchanged today.
Global Expansion
From the 17th century onward, English spread globally, primarily due to the influence of the British Empire and later the United States. English became the dominant language of international discourse and a lingua franca in various professional contexts through printed and electronic media.

Modern English Characteristics
Modern English, as we know it today, relies heavily on auxiliary verbs and word order to convey complex tenses, aspects, and moods. It retains some inflectional elements but has shifted towards a more analytic structure than its earlier stages.
Language Isolation and Influences
English’s development in the British Isles set it apart from continental Germanic languages, leading to significant divergence. While some affinities exist between English and languages like Dutch and Frisian, English is not mutually intelligible with any of them.
Throughout its history, English has been influenced by many invasions and migrations, including those by Old Norse and Norman French speakers. These influences have left their mark on the language, contributing to its rich vocabulary and grammar. However, English is not considered an actual mixed language, though it exhibits elements of Creole-like development.
Classification and Relatives
English belongs to the West Germanic group of the Germanic languages. Its closest living relatives are the Frisian languages, with which it forms the Anglo-Frisian group. Additionally, Low German/Low Saxon is closely related to English, and these languages, along with Frisian, are sometimes grouped as the Ingvaeonic (North Sea Germanic) languages.
Historical Context
The English language has a complex history, shaped by migrations, invasions, and cultural exchanges. From its humble beginnings as Old English to its current status as a global lingua franca, English’s evolution is a testament to its adaptability and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – English Language
These FAQs provide an overview of the English language’s history, development, and global significance.
What is the origin of the English language?
English is a West Germanic language that originated in early medieval England. It developed from a group of North Sea Germanic dialects brought to Britain by Germanic tribes like the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes in the 5th century.
How widely is English spoken today?
English is currently the most spoken language in the world and ranks as the third most spoken native language, following Mandarin Chinese and Spanish. It is also the most widely learned second language, with over two billion speakers as of 2005.
What is the significance of the name “English”?
English is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to Great Britain. People who speak English are referred to as Anglophones.
Where is English primarily spoken?
English is the primary language in the Anglosphere, which includes the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and the Republic of Ireland. It is also widely spoken in various Caribbean, Africa, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Oceania regions.
Is English an official language in international organizations?
English is a co-official language in international organizations like the United Nations and the European Union. It is also an official or one of the official languages in 59 sovereign states.
How did Old English evolve into Modern English?
Old English, which emerged among the Anglo-Saxons in Britain, evolved into Middle English. During this transformation, it absorbed vocabulary from Old Norse and French dialects. Modern English subsequently developed from Middle English.
Is English mutually intelligible with other Germanic languages?
No, English is not mutually intelligible with other continental Germanic languages. While it shares some similarities with Dutch and Frisian, it has diverged considerably due to historical influences from languages like Old Norse and Norman French.
How did external forces impact the development of English?
Other languages and cultures, including Old Norse and Norman French, significantly influenced English. These influences left their mark on English vocabulary and grammar.
Is English considered a mixed language or creole?
Some scholars have suggested that English could be considered a mixed language or creole due to its diverse linguistic influences. However, this theory remains debated, and most specialists do not classify English as a hybrid language.
How is English classified within the Germanic language family?
English belongs to the West Germanic group of the Germanic languages. It is further classified as an Anglo-Frisian language, closely related to Frisian and Low German, and it shares innovations with other Germanic languages like Dutch and German.
What were the significant historical periods of the English language?
The English language evolved through several historical periods, including Old, Middle, and Early Modern English. Distinct linguistic features and influences characterized each of these periods.
How did the development of the English language impact its grammar and vocabulary?
The development of English led to changes in its grammar and vocabulary. It shifted from a highly inflectional language to a more analytic one, relying on word order and auxiliary verbs for expressing complex tenses, aspects, and moods.
What are some famous works from Middle English literature?
Middle English literature includes renowned works like Geoffrey Chaucer’s “The Canterbury Tales” and Thomas Malory’s “Le Morte d’Arthur.” These texts showcase the language’s evolution during the Middle English period.
How did the British Empire and the United States contribute to the global spread of English?
English spread globally in the 17th century due to the influence of the British Empire and the United States. It became the leading language of international discourse and a lingua franca in various fields such as science, navigation, and law.
What are some unique characteristics of Old English compared to Modern English?
Old English featured a more complex inflectional system, including noun cases and verb endings. It was also less standardized in spelling and word order than Modern English.
Is there a connection between English and other Germanic languages like Dutch and German?
Yes, English shares linguistic innovations with other Germanic languages, including dividing verbs into strong and weak classes, using modal verbs, and sound changes known as Grimm’s and Verner’s laws.
How did Old English use runes and Latin alphabets?
In its early stages, Old English used runic scripts for inscriptions, but by the 6th century, it adopted the Latin alphabet. This Latin alphabet included runic and modified Latin letters like eth (ð) and ash (æ).


