Angola, a vibrant country on the southwestern coast of Africa, has emerged from a tumultuous past to embrace a future filled with immense potential. With a diverse cultural heritage, breathtaking natural landscapes, and a wealth of natural resources, Angola is a testament to resilience and progress. In this article, we will delve into the remarkable transformation of Angola, exploring its history, economy, cultural tapestry, and the opportunities it presents for residents and international investors.

- Official Name: Republic of Angola
- Capital: Luanda
- Population: Approximately 32 million (as of the latest available data)
- Official Language: Portuguese
- Currency: Angolan Kwanza (AOA)
- Area: Approximately 1,246,700 square kilometers
- Major Cities: Luanda (capital), Huambo, Benguela, Lubango, Lobito
- Government: Unitary dominant-party presidential republic
- Current President: João Lourenço
- Independence: From Portugal on November 11, 1975
- National Day: November 11 (Independence Day)
- Geography: Angola is located in southwestern Africa and has a diverse landscape that includes coastal areas along the Atlantic Ocean, savannahs, highlands, and a portion of the Kalahari Desert.
- Climate: Angola has a varied climate with arid conditions in the south and more tropical conditions in the north.

Historical Background
Angola’s history is shaped by the influences of various indigenous tribes, Portuguese colonization, and protracted civil war. Achieving independence in 1975, Angola faced years of conflict and instability. However, since the end of the civil war in 2002, the country has been committed to rebuilding and revitalizing its infrastructure, economy, and society.
The history of Angola is rich and complex, with evidence of human presence dating back thousands of years. Various ethnic groups, including the Khoisan, Bantu, and Pygmy peoples, originally inhabited the region that is now Angola. These diverse groups developed unique cultures and societies across the region.
In the late 15th century, Portuguese explorer Diogo Cão reached northern Angola’s shores, beginning Portugal’s influence in the area. The Portuguese established trading posts along the coast and engaged in the slave trade, capturing and transporting enslaved Africans to their colonies in the Americas.
Over the centuries, the Portuguese expanded their control inland, encountering resistance from local kingdoms and societies. By the 19th century, the slave trade declined, and Portugal shifted its focus to exploiting natural resources, notably rubber, and minerals.
In the 20th century, nationalist sentiments emerged in Angola and calls for independence from Portuguese rule grew stronger. The Angolan War of Independence, also known as the Portuguese Colonial War, erupted in 1961 and lasted until 1974, when Portugal’s Carnation Revolution led to the end of the dictatorship and the granting of independence to its colonies, including Angola.
However, the newfound independence was short-lived, as Angola plunged into a civil war. The conflict was initially between two major independence movements: the Marxist-Leninist Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA), supported by the Soviet Union and Cuba, and the National Front for the Liberation of Angola (FNLA) and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), both backed by Western powers, including the United States and South Africa.
The civil war in Angola raged for nearly three decades, devastating the country and causing widespread suffering. The conflict ended in 2002 when the government and UNITA signed a peace agreement.
Since the end of the civil war, Angola has focused on rebuilding its economy and infrastructure. The country is rich in natural resources, including oil and diamonds, but faces governance, corruption, and socio-economic inequality challenges.

Economic Growth and Diversification
Angola’s economy has experienced remarkable growth in recent years, primarily driven by its vast natural resource reserves. As one of Africa’s leading oil producers, Angola has successfully leveraged its oil wealth to invest in infrastructure development, education, healthcare, and social programs. Furthermore, the government has recognized the need for economic diversification, focusing on sectors such as agriculture, mining, tourism, and renewable energy to reduce dependence on oil and create sustainable growth.
Angola is a country with significant potential for economic growth and diversification. Historically, Angola’s economy has heavily relied on its oil sector, which accounts for most of its export revenue. However, in recent years, the government has recognized the importance of diversifying the economy to reduce its vulnerability to oil price fluctuations and foster sustainable growth.
Economic growth in Angola has been primarily driven by its oil production, but this has also led to challenges such as over-reliance on a single commodity, limited job opportunities outside the oil sector, and income inequality. To address these issues, the Angolan government has undertaken initiatives to promote diversification and encourage the growth of other sectors.
One key area of focus for economic diversification is agriculture. Angola possesses vast arable land and favorable climate conditions, making it suitable for agriculture. The government has been investing in modernizing agricultural practices, supporting farmers, and encouraging agribusinesses to boost food production and reduce the country’s reliance on food imports.
Another sector with great potential for diversification is the mining industry. Angola is rich in natural resources, including diamonds, gold, copper, iron ore, and rare earth minerals. The government has been working to attract foreign investment and improve the mining regulatory framework to exploit these resources responsibly and sustainably.
Furthermore, the country’s infrastructure development and investment in manufacturing industries are essential to its economic diversification strategy. By improving transportation, energy, and communication networks, Angola aims to create an enabling environment for businesses to thrive and attract foreign direct investment.
Moreover, the development of the tourism sector holds promise as Angola boasts stunning landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and wildlife diversity. Investing in tourism infrastructure and promoting the country’s unique attractions can contribute to economic growth and job creation in the hospitality and service industries.
However, diversification is not without its challenges. Angola faces obstacles such as inadequate infrastructure, bureaucratic hurdles, and corruption, hindering progress. Additionally, transitioning away from an oil-dependent economy requires careful planning and significant investments in education and training to develop a skilled workforce that can support diverse industries.
Angola acknowledges the significance of fostering economic growth and diversification to cultivate a resilient and sustainable economy. By channeling investments into agriculture, mining, tourism, and manufacturing sectors, the nation endeavors to decrease its reliance on oil, striving for a well-rounded and inclusive economy that uplifts all its citizens. By implementing appropriate policies and making strategic investments, Angola can unleash its untapped potential and pave the way toward a prosperous future.

Investment Opportunities
Angola presents a range of promising investment opportunities across multiple sectors. With its fertile land and favorable climate, the agricultural industry offers immense potential for commercial farming, agribusiness, and food processing. The mining industry, abundant in diamonds, gold, iron ore, and copper, attracts international investors seeking mineral exploration and extraction ventures. The tourism sector, with its breathtaking landscapes, wildlife reserves, and cultural heritage sites, is ripe for investment in hospitality, ecotourism, and infrastructure development.
Angola offers several investment opportunities across various sectors. Despite facing economic challenges due to its heavy reliance on oil revenue, the government has actively promoted diversification and attracted foreign investment in non-oil sectors to drive economic growth.
1. Agriculture: Angola has vast untapped agricultural potential. With fertile lands and a favorable climate, there are opportunities for investment in agribusiness, including crop cultivation, livestock farming, and food processing. The government has implemented policies to support the sector and encourage private investment.
2. Infrastructure: There is a significant need for infrastructure development in Angola, including roads, ports, railways, and energy facilities. The government has actively sought public-private partnerships (PPPs) to finance and execute large-scale infrastructure projects.
3. Mining: Angola possesses significant mineral resources, such as diamonds, iron ore, gold, and copper. The mining sector offers investment opportunities in the exploration, production, and export of these valuable resources.
4. Tourism: Angola’s beautiful landscapes, diverse wildlife, and cultural heritage make it an attractive destination for tourism development. Investment in hotels, resorts, and other tourism-related infrastructure is rising.
5. Renewable Energy: With a growing demand for electricity and a focus on sustainable development, the renewable energy sector offers investment opportunities in solar, wind, and hydropower projects.
6. Manufacturing: Angola aims to reduce import dependence and promote domestic production. There are opportunities for investors in various manufacturing industries, including textiles, food processing, and consumer goods.
7. Technology and Telecommunications: Angola’s rapidly growing young population drives modern technology and telecommunications services demand. Investing in telecommunications infrastructure and digital solutions could be lucrative.
8. Financial Services: As the economy diversifies, the demand for financial services such as banking, insurance, and investment management is increasing. There are opportunities for companies looking to enter this growing market.
9. Real Estate: The demand for housing and commercial spaces in urban centers is rising with the country’s economic development. Real estate investment can be profitable, especially in major cities like Luanda.
It is essential to note that investing in Angola may come with some challenges, including bureaucratic hurdles, corruption, and regulatory complexities. Therefore, potential investors should conduct thorough research, seek expert advice, and carefully assess the risks and rewards before committing to any investment opportunity. As the economic landscape may have changed since my last update, it is advisable to consult up-to-date sources and local authorities for the most current information.
Cultural Diversity and Heritage
Angola is a melting pot of diverse ethnic groups, each contributing to the country’s vibrant cultural tapestry. The blend of traditions, languages, music, and cuisine reflects the richness of Angola’s heritage. Visitors to Angola can explore the captivating rhythms of traditional Angolan music, witness vibrant dance performances, and savor the flavors of local cuisine. The country’s cultural festivals, such as the Carnival in Luanda and the Festival of Mucanda in Huambo, glimpse the spirit and joy of Angolan celebrations.
Angola boasts a rich and diverse cultural heritage shaped by its long history of various ethnic groups, colonization, and struggles for independence. The country’s cultural landscape is a tapestry of traditions, languages, music, dance, art, and cuisine.
1. Ethnic Diversity: Angola is home to over 90 different ethnic groups, each with its unique cultural practices, languages, and traditions. Some of the major ethnic groups include the Ovimbundu, Kimbundu, Bakongo, and Lunda-Chokwe. This diversity has played a significant role in shaping the country’s cultural identity.
2. Language: Angola is a linguistically diverse nation with numerous indigenous languages spoken throughout the country. Portuguese is the official language and is a unifying factor, while regional languages are still widely spoken and celebrated.
3. Music and Dance: Music plays a vital role in Angolan culture, with various traditional and contemporary genres. Semba, Kizomba, Kuduro, and Rebita are popular conventional music styles, while modern genres like Hip-hop and Afro-house have gained popularity in recent years. Dance is integral to the Angolan cultural experience, with expressive movements and rhythms reflecting the nation’s history and traditions.
4. Arts and Crafts: Angolan arts and crafts reflect the creativity and talent of the local artisans. Traditional pottery, basket weaving, wood carving, and beadwork are some of the prominent craft traditions passed down through generations.
5. Festivals and Celebrations: Angolans celebrate various cultural and religious festivals, each showcasing their unique customs and beliefs. Festivals like Mwila-Ku-N’Ginga, Luanda International Jazz Festival, and FESTIKONGO are celebrated with music, dance, and feasts.
6. Cuisine: Angolan cuisine is a delicious fusion of indigenous flavors, Portuguese influences, and international influences. Dishes like Muamba de Galinha (chicken stew), Calulu (dried fish with vegetables), and Funje (cassava porridge) are staples of Angolan culinary heritage.
7. Heritage Sites: Angola’s cultural heritage is also reflected in its historical sites and landmarks. Examples include the Mbanza Kongo, the former capital of the Kongo Kingdom and a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and the Cuito Cuanavale Battlefield, which played a crucial role in the country’s struggle for independence.
8. Oral Traditions: Oral traditions are essential to preserving Angola’s cultural heritage. Storytelling, proverbs, and folktales are passed down through generations, transmitting knowledge, values, and history.
Despite experiencing challenges during years of civil conflict, Angola’s cultural diversity and heritage have endured and continue to be celebrated. Embracing and preserving these traditions are vital for maintaining the country’s unique identity and fostering a sense of unity and pride among its people.
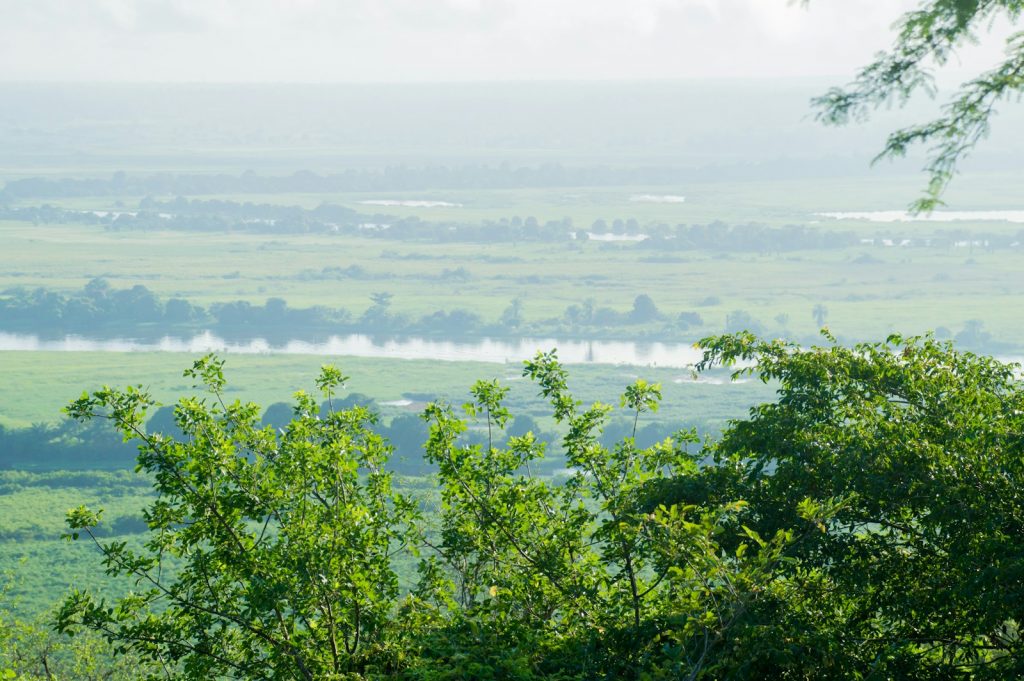

Natural Wonders and Ecotourism
Angola boasts an array of natural wonders, from the magnificent Kalandula Falls to the pristine beaches of the Benguela coastline. The country’s national parks, such as Quiçama National Park and Bicuar National Park, offer wildlife safaris, birdwatching, and eco-adventure opportunities. Angola’s commitment to environmental conservation and ecotourism presents a chance for sustainable tourism initiatives, promoting economic growth and preserving its unique biodiversity.
Angola boasts diverse natural wonders, making it a promising destination for ecotourism enthusiasts. Despite being less explored than some neighboring countries, Angola’s untamed landscapes offer unique and awe-inspiring experiences for those seeking adventure and a deeper connection with nature.
1. Iona National Park: This expansive national park, located in the southern part of Angola, is a biodiverse haven that encompasses vast desert dunes, rugged mountains, and striking coastal plains. Visitors can witness a rich array of wildlife, including rare desert-adapted elephants, lions, oryx, and springboks. The remote and untouched nature of Iona National Park makes it an appealing destination for eco-conscious travelers.
2. Kalandula Falls: As one of the largest waterfalls in Africa, Kalandula Falls is a breathtaking natural wonder. The cascading waters plummet from around 105 meters (344 feet), creating a mesmerizing sight amidst lush green surroundings. The falls provide a stunning spectacle and opportunities for outdoor activities like hiking and birdwatching.
3. Kissama National Park: Situated close to Angola’s capital city, Luanda, Kissama National Park offers a convenient escape into nature. The park’s diverse habitats support a variety of wildlife, including elephants, buffaloes, giraffes, and antelopes. Visitors can partake in guided safaris and boat tours along the Kwanza River to observe this remarkable area’s fascinating flora and fauna.
4. Tundavala Gap: Located in the Huíla Province, the Tundavala Gap offers dramatic views of a vast escarpment that stretches as far as the eye can see. This geological wonder provides an ideal setting for hiking and trekking adventures. The surrounding area is also known for its unique endemic plant species, making it an attractive destination for botanists and nature enthusiasts.
5. Namibe Desert: Angola’s Namibe Desert, along the country’s southwestern coast, is a captivating and otherworldly landscape of vast dunes and rocky plateaus. The desert’s arid beauty offers serene contemplation and stargazing under apparent skies.
6. Bicuar National Park: In southeast Angola lies Bicuar National Park, a sanctuary for diverse wildlife species. The park is renowned for its birdlife, housing numerous species of migratory and resident birds. Game drives through the park allow one to spot elephants, zebras, and wildebeests roaming in their natural habitat.
Ecotourism in Angola is still early, offering visitors a chance to explore relatively untouched areas and contribute to the country’s conservation efforts. While visiting these natural wonders, travelers must prioritize responsible and sustainable practices to preserve Angola’s unique ecosystems for generations.

Conclusion
Angola has embarked on a transformative journey, turning challenges into opportunities and fostering an environment conducive to progress. With its thriving economy, cultural diversity, and breathtaking natural landscapes, Angola invites the world to explore its potential. From investors seeking promising ventures to travelers eager to discover hidden gems, Angola promises a rewarding experience for those willing to embrace its wealth of opportunities. As Angola continues to build a brighter future, it stands as a shining example of resilience, growth, and the indomitable spirit of the African continent.
FAQ
Q: Where is Angola located?
A: Angola is located on the southwestern coast of Africa.
Q: What is the capital city of Angola?
A: The capital city of Angola is Luanda.
Q: What is the official language of Angola?
A: The official language of Angola is Portuguese.
Q: What is the population of Angola?
A: As of 2021, the estimated population of Angola is over 32 million people.
Q: What is the currency used in Angola?
A: The currency used in Angola is the Angolan kwanza (AOA).
Q: What is the climate like in Angola?
A: Angola has a varied climate, ranging from tropical in the north to semi-arid in the south. The country experiences distinct wet and dry seasons.
Q: What are the primary natural resources of Angola?
A: Angola is rich in natural resources, with oil being the most significant. Other resources include diamonds, gold, iron ore, copper, and agricultural products such as coffee and cocoa.
Q: Is Angola a safe country to visit?
A: While Angola has made significant progress in safety and security, it is advisable to exercise caution and stay informed about the current situation before traveling. It is always recommended to follow travel advisories and take necessary precautions.
Q: What are the popular tourist attractions in Angola?
A: Angola offers diverse tourist attractions, including the Kalandula Falls, the Kissama National Park, the Namibe Desert, the historic city of Mbanza Kongo, the Benguela coastline, and the Iona National Park, among others.
Q: What is the official religion of Angola?
A: There is no official religion in Angola. Most of the population practices Christianity, with Roman Catholicism as the predominant denomination.
Q: What is the transportation system like in Angola?
A: Angola has a developing transportation system. Roads connect major cities, and there are domestic flights available. However, infrastructure outside urban areas can be limited, and planning transportation arrangements in advance is advisable.
Q: What is the current political situation in Angola?
A: Angola is a presidential republic. The country has undergone significant political changes and is currently led by President João Lourenço, who assumed office in 2017.
It is always recommended to refer to up-to-date sources and consult official travel advisories before making any travel plans.


