Unveiling Coffee’s Global Impact: A Fascinating Look at Coffee Statistics
Coffee, the beloved beverage millions consume worldwide, has a rich history and an enduring presence in our daily lives. From humble beginnings as a traditional drink in Ethiopia to becoming a global phenomenon, coffee has played a significant role in various cultures and economies. This article delves into coffee statistics, exploring its consumption patterns, economic significance, and environmental impact. Drawing from reliable sources, we uncover intriguing insights that shed light on the fascinating world of coffee.
1. Global Coffee Consumption:
Coffee is undeniably one of the most consumed beverages globally, with staggering statistics supporting its popularity. According to the International Coffee Organization (ICO), in 2021, an estimated 166 million 60-kilogram bags of coffee were consumed worldwide. This figure represents an increase of 1.9% compared to the previous year, highlighting the consistent growth in coffee consumption.
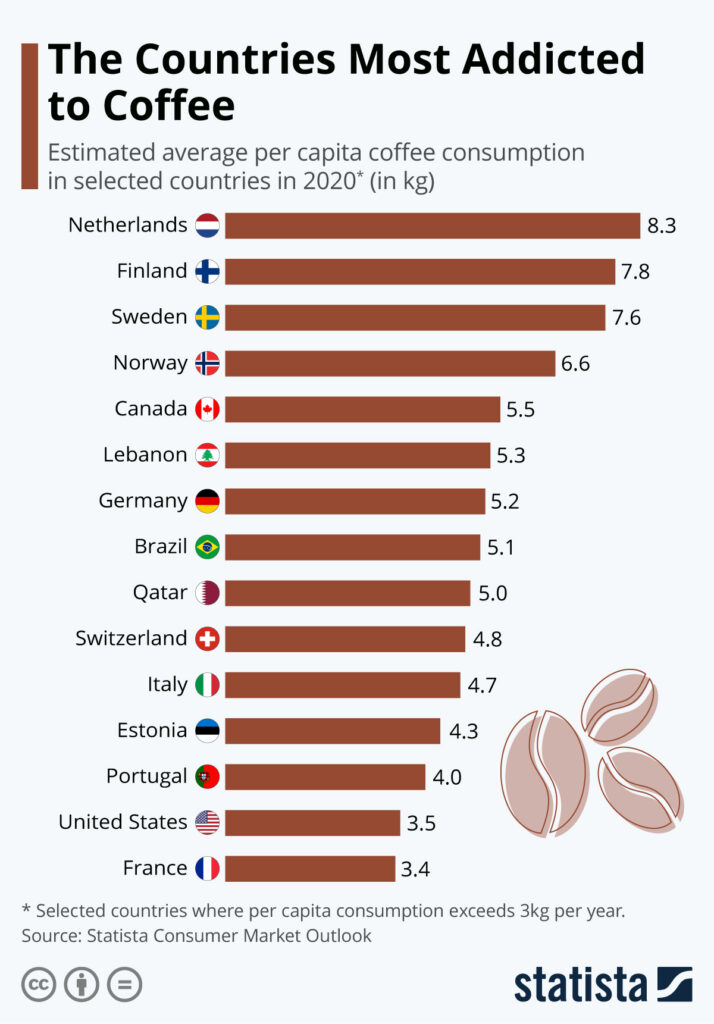
2. Top Coffee Consumers:
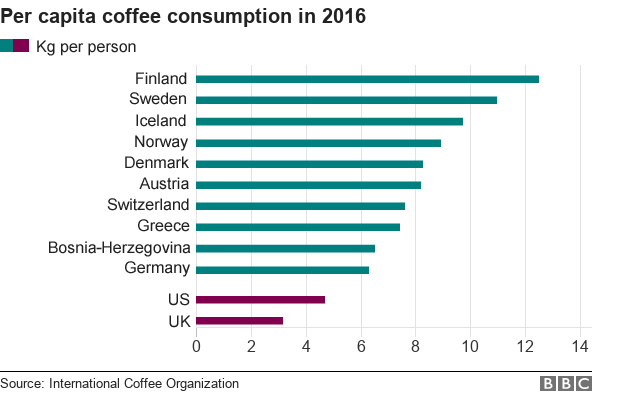
When it comes to the largest coffee-consuming nations, Europe takes the lead. Renowned for its coffee culture, Finland holds the top spot with an astonishing average annual per capita consumption of over 12 kilograms. Other countries that rank high on the list include Sweden, Switzerland, and Norway. The United States dominates the scene in North America, consuming approximately 26 million bags of coffee annually.
3. Economic Significance:
Coffee’s economic impact extends far beyond the boundaries of the countries that produce it. According to the ICO, coffee is one of the most valuable agricultural commodities in the world. In terms of trade, coffee exports generated a staggering $21.6 billion in revenue in 2020. It is worth noting that coffee cultivation and production provide a livelihood for millions of farmers in developing countries, making it a crucial aspect of their economies.

4. Environmental Concerns:
The production of coffee has raised concerns about its environmental impact, specifically regarding deforestation and carbon emissions. The need for land to cultivate coffee has contributed to deforestation in certain regions, leading to the loss of vital ecosystems. Various sustainability initiatives have been introduced to combat this issue, such as the Rainforest Alliance and Fairtrade certification programs, which promote environmentally responsible coffee production practices.
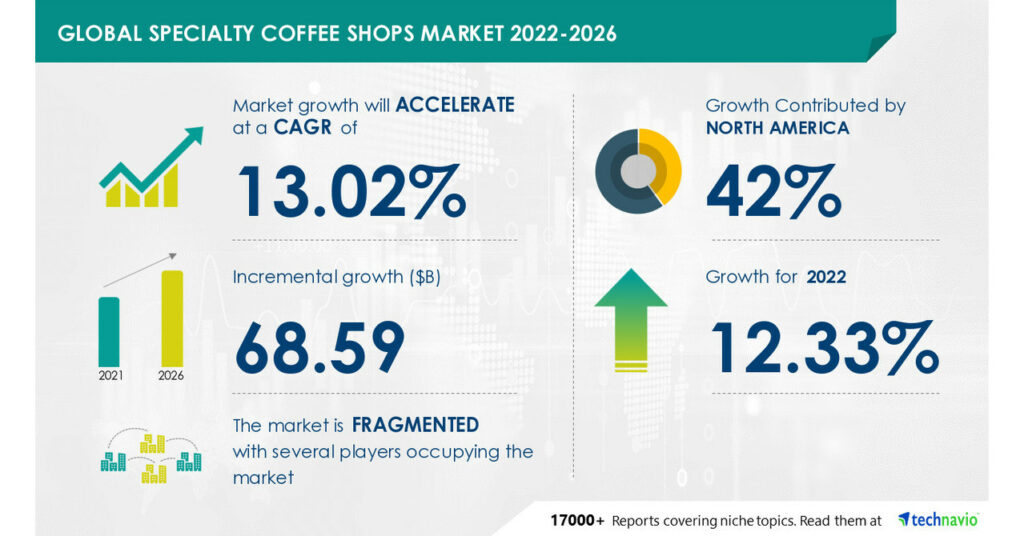
5. Specialty Coffee on the Rise:
In recent years, the specialty coffee market has experienced remarkable growth. Specialty coffee refers to coffee produced and prepared with exceptional quality standards, focusing on unique flavors, brewing methods, and traceability. According to the Specialty Coffee Association (SCA), the specialty coffee market represents approximately 25% of the global coffee market, with consumers increasingly seeking distinctive and ethically sourced coffee experiences.
6. Coffee and Health:
Coffee has long been studied for its potential effects on human health. Numerous scientific studies have explored coffee consumption’s health benefits and risks. Moderate coffee intake has been linked to reduced risks of certain diseases such as Parkinson’s, type 2 diabetes, and liver disease. However, it is essential to note that individual responses to coffee can vary, and excessive consumption may have adverse effects, such as insomnia or increased heart rate.

The world of coffee is a vibrant tapestry of consumption patterns, economic significance, environmental concerns, and health considerations. As coffee continues to captivate our senses and play a significant role in our daily lives, it is essential to understand the global statistics that underpin this remarkable beverage. With its rich history and global impact, coffee is more than a simple drink; it is a cultural symbol, an economic force, and a source of delight for millions worldwide.
Watch Video
FAQ
Q1: Is coffee addictive?
A1: Coffee contains caffeine, a stimulant that can lead to mild physical dependence. Regular coffee drinkers may experience withdrawal symptoms, such as headaches or fatigue if they abruptly stop consuming caffeine.
Q2: How much caffeine is in a cup of coffee?
A2: The caffeine content in coffee can vary depending on factors like the brewing method and the type of coffee beans used. On average, an 8-ounce (240 ml) cup of coffee contains around 95 mg of caffeine, but it can range from 30 to over 200 mg.
Q3: Can coffee help improve focus and alertness?
A3: Yes, coffee is known for its stimulant properties. Caffeine can enhance mental alertness, improve focus, and temporarily reduce fatigue. However, individual responses to caffeine may vary.
Q4: Does coffee have any health benefits?
A4: Moderate coffee consumption has been associated with several potential health benefits. Studies suggest that coffee may help protect against certain diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, type 2 diabetes, liver disease, and certain types of cancer. It may also contain antioxidants that contribute to overall health.
Q5: Does coffee cause dehydration?
A5: Contrary to popular belief, moderate coffee consumption does not cause dehydration. While coffee has mild diuretic effects, its water content is sufficient to offset its potential diuretic impact. It can contribute to your daily fluid intake, but excessive consumption should be avoided.
Q6: Can coffee interfere with sleep?
A6: Yes, consuming coffee close to bedtime can interfere with sleep. The stimulating effects of caffeine can make it difficult to fall asleep and may disrupt sleep quality. Limiting coffee intake in the evening or switching to decaffeinated options is recommended.
Q7: Is coffee safe for pregnant women?
A7: Pregnant women are advised to limit their caffeine intake, including coffee. High caffeine consumption during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of miscarriage and low birth weight. It is best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Q8: Does the roast level affect the caffeine content in coffee?
A8: Contrary to popular belief, the roast level of coffee beans does not significantly affect the caffeine content. The difference in caffeine between light and dark roast coffees is minimal, as the roasting process mainly involves the flavor and aroma of the coffee.
Q9: Can coffee cause stomach issues?
A9: Coffee can be a common trigger for gastrointestinal issues in some individuals. The acidity and caffeine content in coffee may lead to acid reflux, heartburn, or stomach discomfort, especially on an empty stomach. Choosing low-acid or decaffeinated coffee and consuming it with food can help reduce these effects.
Q10: Are there any alternatives to traditional coffee for those sensitive to caffeine?
A10: Several alternatives are available for those who prefer to avoid or limit caffeine intake. Decaffeinated coffee, herbal teas like chamomile or peppermint, and caffeine-free coffee substitutes like chicory or herbal blends can provide a coffee-like experience without caffeine.
Citations
1. International Coffee Organization (ICO) – Official website providing comprehensive coffee market statistics and reports: https://www.ico.org/
2. Statista – A trusted source for global coffee consumption statistics and industry trends: https://www.statista.com/
3. National Coffee Association (NCA) – Offers valuable insights and data on coffee consumption and industry trends in the United States: https://www.ncausa.org/
4. Specialty Coffee Association (SCA) – Provides information and research on specialty coffee trends, including market statistics and consumer preferences: https://sca.coffee/
5. World Coffee Research (WCR) – A nonprofit organization focused on coffee research and sustainability, offering valuable data on coffee production and environmental impact: https://worldcoffeeresearch.org/
6. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations – Provides reports and statistics on coffee production, trade, and sustainability: http://www.fao.org/home/en/
7. International Trade Centre (ITC) – Offers market intelligence, trade statistics, and analysis on coffee exports and imports worldwide: https://www.intracen.org/
8. European Coffee Federation (ECF) – Provides data and insights on coffee consumption patterns and trends in Europe: https://europeancoffeefederation.org/
9. United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) – Offers information on coffee production, consumption, and trade, including global market data: https://www.usda.gov/
10. Coffee Barometer – An initiative that provides in-depth reports on sustainability issues in the coffee sector, including relevant statistics: https://www.coffeebarometer.org/


