Albania, officially known as the Republic of Albania, is a small but fascinating country in Southeastern Europe. Albania shares borders with Montenegro, Kosovo, North Macedonia, and Greece in the Balkan Peninsula. This article provides an in-depth perspective on Albania, exploring its history, natural beauty, cultural heritage, and more.

Geography and Natural Beauty
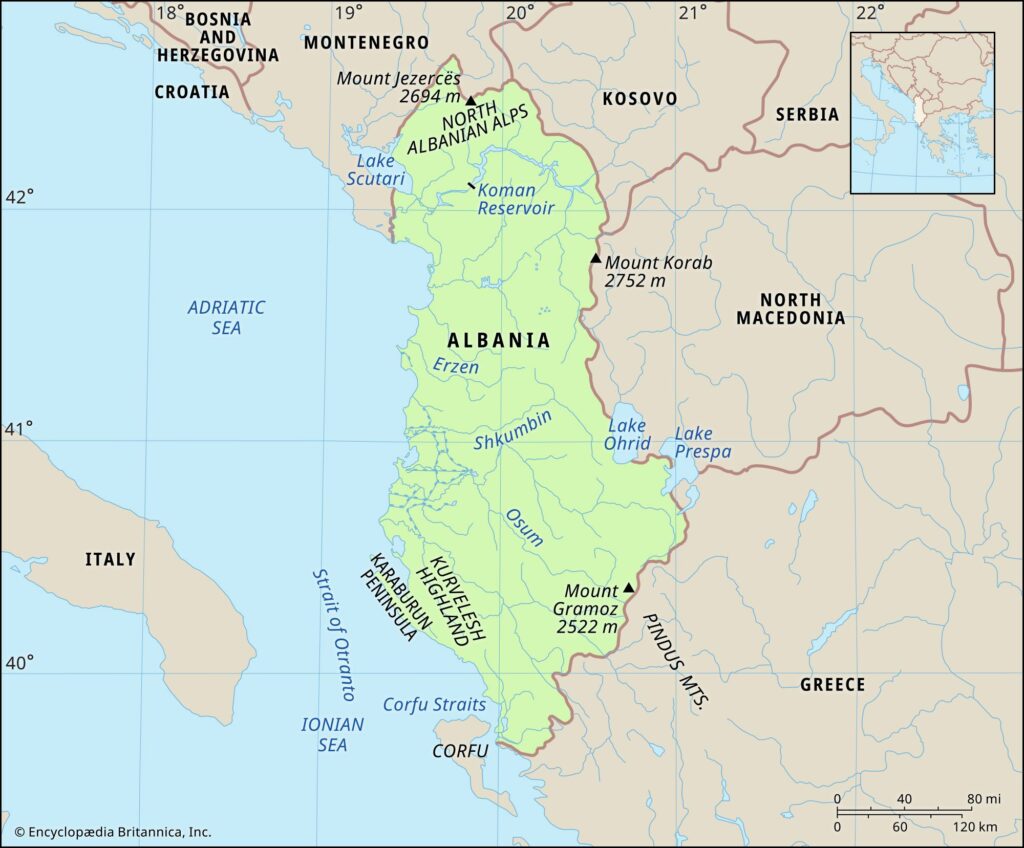
Albania boasts diverse geographical features covering an area of approximately 28,748 square kilometers. Bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east, and Greece to the south, Albania boasts a stunning coastline along the Adriatic Sea to the west and the Ionian Sea to the southwest.
The most remarkable feature of Albania’s geography is its rugged landscape. The country is characterized by mountain ranges: the Albanian Alps in the north, the Sharr Mountains in the east, and the Pindus Mountains in the south. These majestic mountains offer breathtaking views, ample hiking opportunities, and picturesque alpine villages.
Albania is also home to numerous rivers and freshwater lakes, such as Lake Shkodra, one of the largest in the Balkans, and Lake Ohrid, a UNESCO World Heritage Site it shares with North Macedonia. These bodies of water provide stunning scenery and recreational activities like boating, fishing, and birdwatching.
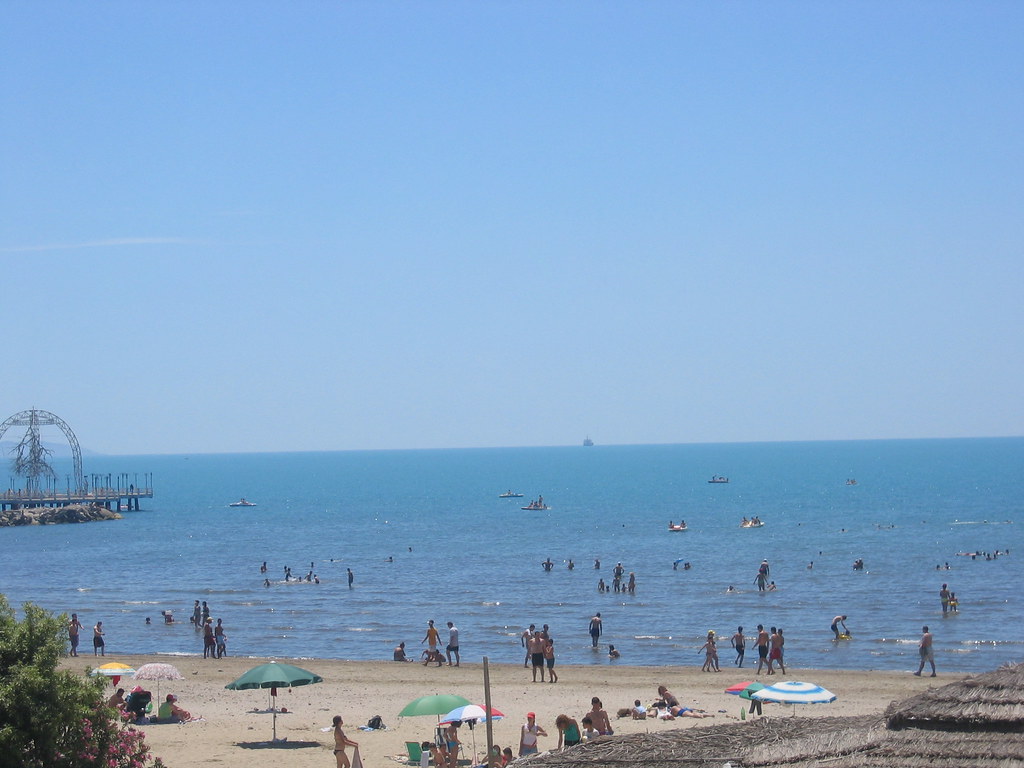
The coastal regions of Albania are renowned for their pristine beaches and crystal-clear waters, making them an increasingly popular destination for tourists seeking a less crowded alternative to other Mediterranean hotspots. From the sandy shores of Durres and Vlora to the more secluded coves of the Albanian Riviera, the country’s coastline is a hidden gem waiting to be discovered.
Albania boasts a rich biodiversity and is home to numerous protected areas and national parks. The Butrint National Park, another UNESCO World Heritage Site, preserves ancient ruins, flora, and fauna. The Valbona Valley National Park, located in the Albanian Alps, is a paradise for nature enthusiasts, offering outstanding hiking and wildlife observation opportunities.
Beyond its natural beauty, Albania’s geography has influenced its culture, history, and traditions. The mountains, for instance, have led to the development of isolated communities and unique cultural practices that have persisted for centuries.
In conclusion, Albania’s geography and natural beauty combine to create a country of extraordinary landscapes and diverse experiences. From the towering mountains to the pristine beaches and lush valleys, Albania offers an abundance of natural wonders that continue to captivate and enthrall visitors worldwide.
History and Cultural Heritage
Ancient times: The region that is now Albania was inhabited by the Illyrians, an old Indo-European people dating back to around 2000 BCE. They were known for their skilled craftsmanship, particularly in metalwork. The Greeks and Romans also had a significant presence in the area, leaving behind archaeological sites and cultural influences.
Middle Ages: In the early Middle Ages, Albania came under the influence of the Byzantine Empire, which heavily influenced the country’s language and religion. During this period, the area experienced the rise of various principalities and feudal states.
Ottoman rule: In the 15th century, the Ottomans conquered Albania, and their control endured for almost five centuries. During this extended period, Islam emerged as the predominant religion, constructing numerous mosques and religious edifices. Despite living under Ottoman rule, Albanians safeguarded their language, customs, and unique identity, showcasing their resilience and cultural strength.
National Awakening and Independence: In the 19th century, a national awakening occurred in Albania, leading to the Albanian National Revival. Intellectuals and patriots sought to preserve Albanian culture and language and work towards independence. On November 28, 1912, Albania declared independence from the Ottoman Empire.
Interwar period and communism: Albania faced a turbulent period after gaining independence, including territorial disputes and political instability. In 1944, communist forces led by Enver Hoxha took control, and Albania became a communist state. Hoxha’s regime imposed strict isolationist policies, which severed Albania from the rest of the world for several decades.
Post-communism era: With the fall of communism in 1991, Albania embarked on a journey of political and economic transformation. The country faced numerous challenges but slowly transitioned into a democratic society and opened up to the international community.
Cultural heritage: Albania boasts a vibrant cultural heritage, encompassing traditional music, dance, cuisine, and crafts. Various instruments, including the çifteli and lahuta characterize Albanian folk music. The country is also renowned for its unique polyphonic singing, recognized as a UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.
Albania’s rich history is evident in its archaeological sites, castles, churches, and mosques scattered throughout the country. Notable cultural landmarks include the ancient city of Butrint, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and the Gjirokastër and Berat, both historic towns with well-preserved Ottoman architecture.
Albania’s history and cultural heritage play a crucial role in shaping the national identity of its people as they continue to embrace their past while embracing a future of progress and integration into the global community.

Archaeological and Historic Sites
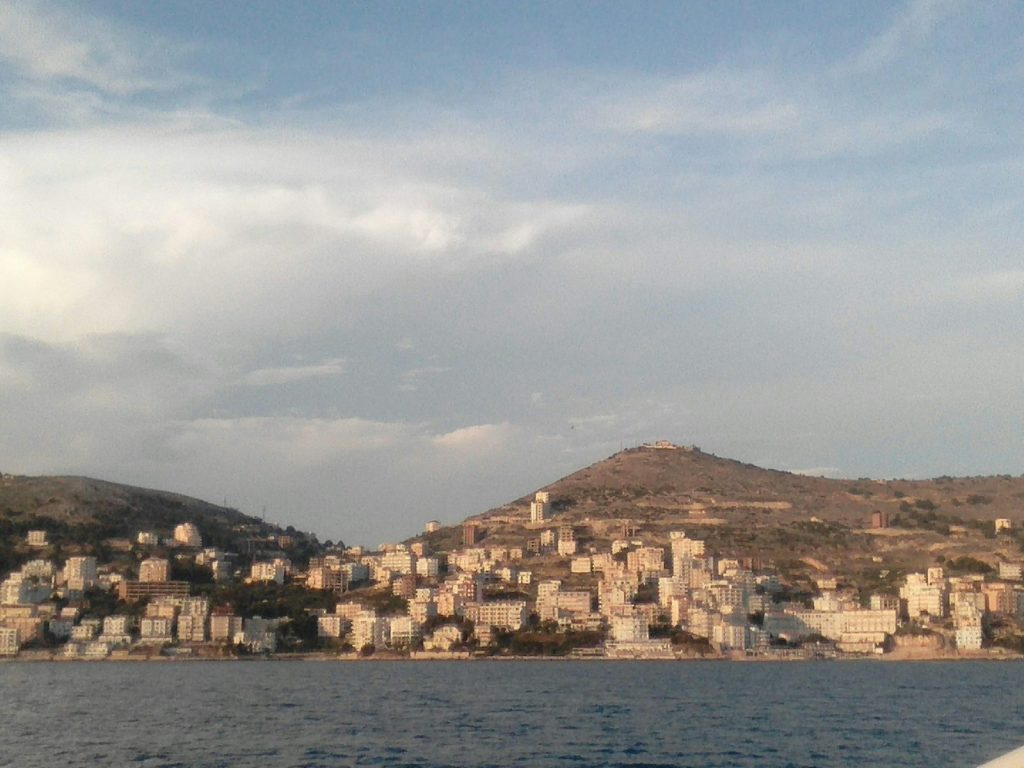
Albania, a country in the Balkans with a rich and diverse history, is home to numerous archaeological and historic sites that showcase its ancient past and cultural heritage. Some of the most notable sites include:
1. Butrint: Located in southern Albania, Butrint is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the country’s most important archaeological parks. The Illyrians founded this ancient city, which was later occupied by the Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, and Venetians. The site features impressive ruins, including a theater, Roman baths, and a baptistery.
2. Apollonia: Another significant archaeological site, Apollonia, was a prominent Greek colony and later a Roman city. It was named after the god Apollo and was an essential center of learning in antiquity. Today, visitors can explore its ancient walls, temples, and the well-preserved Odeon.
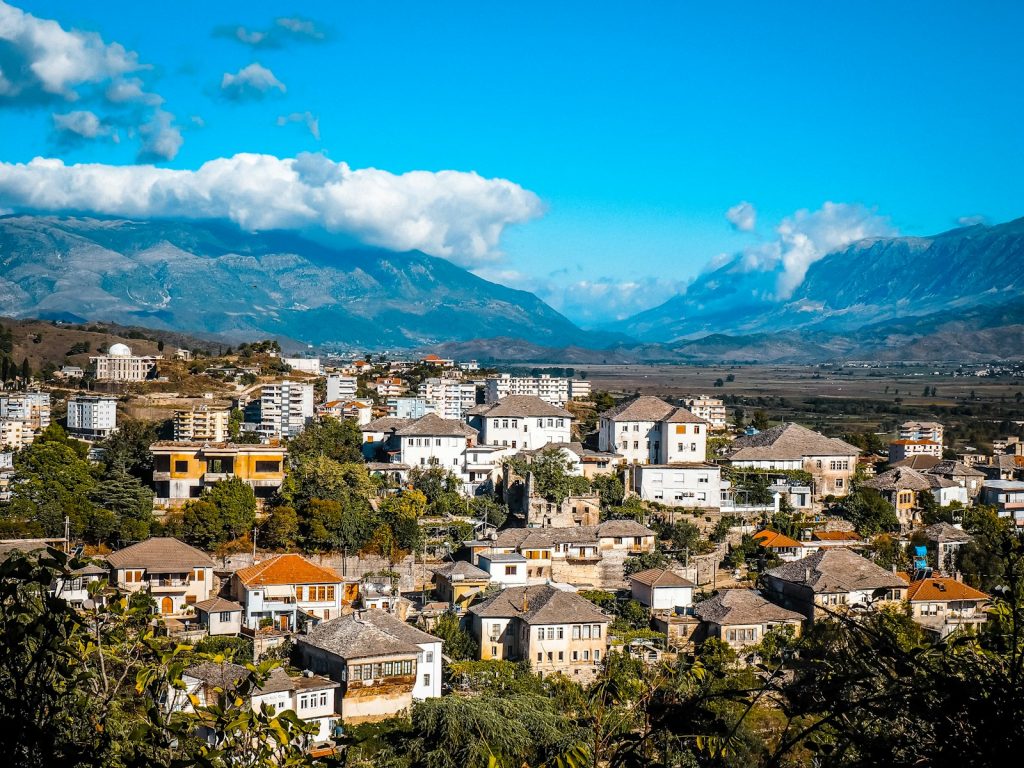
3. Gjirokastër: This city is a UNESCO World Heritage Site renowned for its well-preserved Ottoman architecture. Its historic center is filled with traditional stone houses, narrow cobbled streets, and the imposing Gjirokastër Castle, which dates back to the 12th century.
4. Berat: Often called the “City of a Thousand Windows,” Berat is another UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of Albania’s oldest continuously inhabited cities. Its well-preserved Ottoman houses, medieval churches, and the 13th-century Berat Castle make it a captivating destination.
5. Byllis: The ancient city of Byllis dates back to the 4th century BC and was an important center during Hellenistic and Roman times. The site contains remains of temples, a theater, and a Byzantine church.
6. Shkodër: As one of Albania’s oldest cities, Shkodër boasts a rich history. It was an Illyrian settlement and later a Roman city. The Rozafa Castle, situated on a hill overlooking the town, offers breathtaking views and has layers of history dating back to Illyrian times.
7. Antigonea: Founded by King Pyrrhus of Epirus in honor of his wife, Antigonea is an ancient city known for its well-planned layout and defensive walls. It was an essential political and cultural center in the region.
These are just a few examples of the many archaeological and historical sites that Albania has to offer. Exploring these sites provides a fascinating journey through the country’s past and offers insight into the civilizations that have shaped its cultural identity over millennia.

Vibrant Cities
Albania’s cities are vibrant and bustling, blending old-world charm with modern developments. Tirana, the capital, has undergone significant transformations in recent years, boasting colorful buildings, trendy cafes, and a lively atmosphere: Shkodër, the country’s cultural center, houses museums, theaters, and historical landmarks. The coastal city of Vlorë attracts visitors with its beautiful beaches and historical significance as the site where Albania declared its independence in 1912.
1. Tirana: The capital city and the heart of Albania, Tirana is a dynamic metropolis that has undergone significant transformation in recent years. Colorful buildings, pedestrian-friendly boulevards, and a thriving café culture give Tirana a vibrant and energetic vibe. Skanderbeg Square, the city’s central square, is a popular gathering spot, while the Blloku district is known for its trendy bars, restaurants, and nightlife.
2. Vlora: Located on the country’s southwest coast, Vlora is a coastal city with stunning beaches and a lively waterfront promenade. It is a popular destination for locals and tourists, offering opportunities for water sports, beachfront dining, and exploring nearby historical sites like the ancient city of Apollonia.
3. Shkodra: Known for its rich history and picturesque setting, Shkodra is one of Albania’s oldest and most culturally significant cities. The Rozafa Castle overlooks the city and offers breathtaking views of Lake Shkodra and the surrounding mountains. Shkodra’s old town, with its cobbled streets and traditional architecture, exudes a charming atmosphere.
4. Gjirokaster: A UNESCO World Heritage site, Gjirokaster is a city with a fascinating history and well-preserved Ottoman architecture. The imposing Gjirokaster Castle dominates the skyline, and the old bazaar area is filled with craft shops, restaurants, and artisanal workshops.
5. Durres: As one of the oldest cities in Albania, Durres boasts a rich history dating back to the ancient Roman period. Today, it is a popular coastal destination with beautiful beaches, lively bars, and a vibrant street market.
6. Berat: Often referred to as the “City of a Thousand Windows,” Berat is a captivating city known for its white Ottoman houses cascading down the hillside. The well-preserved medieval architecture and the Berat Castle contribute to its unique charm.
7. Saranda: Situated on the Ionian Sea coast, Saranda is a lively resort town with a relaxed atmosphere. It serves as a gateway to the nearby archaeological site of Butrint, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and the mesmerizing Blue Eye Spring.
Albania’s vibrant cities showcase the country’s diverse cultural heritage and offer visitors a chance to experience the warmth and hospitality of its people. With a mix of historical landmarks, natural beauty, and a burgeoning urban scene, these cities provide a captivating glimpse into Albania’s past and present.

Cuisine and Hospitality
Albanian cuisine and hospitality reflect the country’s rich history and cultural diversity. Albanian food is characterized by a blend of Mediterranean and Balkan influences, focusing on fresh, locally-sourced ingredients.
1. Traditional Dishes: One of the most famous traditional dishes in Albania is “Tavë kosi,” a delicious casserole made with lamb, rice, and yogurt. “Fërgesë” is another well-loved dish with peppers, tomatoes, and cottage cheese cooked together. Seafood is also abundant due to Albania’s coastal location, and dishes like “Baked Shkodra Carp” are cherished delicacies.
2. Olive Oil: Olive oil is a staple in Albanian cuisine and is crucial in flavoring many dishes. Albania boasts numerous olive groves, producing high-quality olive oil used in cooking and as a dressing for salads and other dishes.
3. Hospitality: Albanian hospitality is renowned for its warmth and generosity. Guests are often treated with great respect and offered abundant food and drinks. Serving multiple courses during meals is customary, reflecting the importance of sharing and community in Albanian culture.
4. Coffee Culture: Albania has a vibrant coffee culture influenced by the Ottoman era. Coffeehouses are popular social hubs where locals gather to chat, play games, or enjoy rich, strong coffee.
5. Baklava and Sweets: Albanian desserts delight the taste buds, with baklava being a favorite. This sweet pastry, made with layers of phyllo dough, nuts, and syrup, is a must-try. Other popular sweets include “Sheqerpare” (Albanian butter cookies) and “Trilece” (a sponge cake soaked in sweet milk).
6. Regional Variations: Albania’s cuisine also varies regionally. In the north, you’ll find heartier dishes influenced by Balkan flavors, while Mediterranean influences are more prevalent in the south, emphasizing seafood and lighter fare.
7. Culinary Festivals: Albania celebrates its gastronomic traditions through various food festivals held throughout the year. These events showcase local dishes, wines, and other delicacies, offering visitors a chance to experience the country’s rich culinary heritage.
In recent years, Albanian cuisine has gained international recognition, attracting tourists eager to savor its unique flavors and experience the genuine hospitality of the Albanian people. Whether you’re dining in a family home or a local restaurant, the taste of Albania is sure to leave a lasting impression.

Tourism Potential and Future
With its stunning landscapes, rich history, and unique cultural heritage, Albania offers diverse experiences that cater to various interests.
1. Natural Beauty: Albania is blessed with abundant natural beauty. It boasts a stunning coastline along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas, with pristine beaches, crystal-clear waters, and picturesque coastal towns like Saranda and Ksamil. Inland, the country is adorned with majestic mountains, including the Albanian Alps in the north and the scenic Zagoria region. Nature enthusiasts, hikers, and adventure seekers find a paradise in Albania’s untouched wilderness.
2. Cultural and Historical Heritage: Albania’s history spans thousands of years, leaving behind a wealth of archaeological sites, ancient ruins, and well-preserved Ottoman and Byzantine architecture. Notable historical sites include the UNESCO World Heritage-listed old city of Butrint, the UNESCO-protected Gjirokastër and Berat with their unique Ottoman-style houses, and the Roman amphitheater in Durrës.
3. Authentic Experiences: Unlike some crowded tourist destinations, Albania still offers an authentic and unspoiled experience. Visitors can immerse themselves in the local culture, try traditional Albanian cuisine, and interact with warm and hospitable locals.
4. Emerging Tourism Infrastructure: In recent years, Albania has been investing in its tourism infrastructure, including better roads, improved accommodation options, and the development of new attractions and activities. This has helped to enhance the overall travel experience and attract more tourists.
5. Adventure and Outdoor Activities: The diverse landscapes of Albania provide ample opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts. Activities like hiking, trekking, paragliding, and water sports are gaining popularity among adventure seekers.
6. Sustainable Tourism Potential: Albania’s relatively untouched nature offers a significant advantage for promoting sustainable tourism practices. Responsible tourism initiatives are encouraged to preserve the country’s natural and cultural assets for future generations.
As for the future of tourism in Albania, the country needs to balance development and preserve its unique identity. Sustainable tourism practices and careful planning are crucial to prevent over-tourism and protect the natural and cultural heritage. Collaborating with local communities to provide economic opportunities while respecting their traditions will be essential.
Furthermore, the Albanian government and tourism industry must focus on marketing and promoting the country as an attractive and safe destination. Targeting specific markets, such as adventure travelers, history enthusiasts, or nature lovers, can help attract niche tourists and maintain a sustainable visitor flow.
In conclusion, Albania’s tourism potential is undeniably promising. With its natural beauty, rich history, and genuine experiences, Albania has the potential to become a must-visit destination in the Balkans. By embracing sustainable practices and careful planning, the country can shape its tourism industry’s successful and responsible future.
Conclusion
With its captivating history, stunning landscapes, and warm hospitality, Albania offers a unique travel experience. From ancient archaeological sites to breathtaking mountains and pristine beaches, the country caters to diverse interests. As Albania emerges as a rising tourist destination, visitors can explore its rich history, immerse themselves in its vibrant culture, and create lasting memories in this enchanting Balkan gem.
FAQ
Q: Where is Albania located?
A: Albania is located in Southeastern Europe, bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east, and Greece to the south. It has a coastline along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas to the west.
Q: What is the capital city of Albania?
A: The capital city of Albania is Tirana. It is the largest city in the country and serves as its political, economic, and cultural center.
Q: What is the official language of Albania?
A: The official language of Albania is Albanian. It is an Indo-European language spoken by most of the population. Albanian has two main dialects: Gheg in the north and Tosk in the south.
Q: What is the currency used in Albania?
A: The currency used in Albania is the Albanian Lek (ALL). It is denoted by the symbol “L” and is the only legal tender in the country. International credit and debit cards are widely accepted in major cities and tourist areas.
Q: Is Albania a safe country to visit?
A: Albania is generally considered a safe country to visit. However, like any destination, it is advisable to take standard safety precautions, such as being aware of your surroundings, securing your belongings, and following local laws and customs. It is also recommended to check travel advisories and consult reliable sources for up-to-date information before your visit.
Q: What are some famous tourist attractions in Albania?
A: Albania offers a range of attractions for visitors. Some famous tourist destinations include the UNESCO World Heritage Sites of Butrint National Park, Berat, and Gjirokastër. The Albanian Riviera attracts beachgoers and sun-seekers with its beautiful beaches and coastal towns like Saranda and Vlorë. Outdoor enthusiasts can explore the Albanian Alps, Theth National Park, and the Valbona Valley. Additionally, the capital city of Tirana has a vibrant nightlife, museums, and historical landmarks.
Q: What is the best time to visit Albania?
A: The best time to visit Albania is spring (April to June) and autumn (September to October) when the weather is mild and pleasant. Summers can be hot, especially along the coast, making it a popular time for beach vacations. Winter months (December to February) can be cold, particularly in the mountainous regions, but offer opportunities for winter sports enthusiasts.
Q: What is the cuisine like in Albania?
A: Albanian cuisine is a mix of Mediterranean and Balkan influences. Traditional dishes often feature fresh local ingredients such as meat, dairy products, vegetables, and seafood. Popular dishes include byrek (a savory pastry), tave kosi (baked lamb with yogurt), fërgesë (a dish with peppers, tomatoes, and cottage cheese), and baklava (a sweet pastry). Albania also produces its own wine and raki (a fruit brandy), which locals and visitors enjoy.
Q: Do I need a visa to visit Albania?
A: The visa requirements for Albania depend on your nationality. Citizens of many countries, including the United States, Canada, the European Union, and several others, can enter Albania for tourism purposes without a visa and stay for up to 90 days within six months. However, checking the visa regulations specific to your country of citizenship is advisable before traveling.
Q: Can I drink tap water in Albania?
A: While tap water in major cities is generally safe to drink, it is recommended to drink bottled water or use water purification methods, especially in more rural areas. Bottled water is readily available and affordable throughout the country.






